-
852 Madurdaha, EKT, Kolkata 700107
852 Madurdaha, EKT, Kolkata 700107
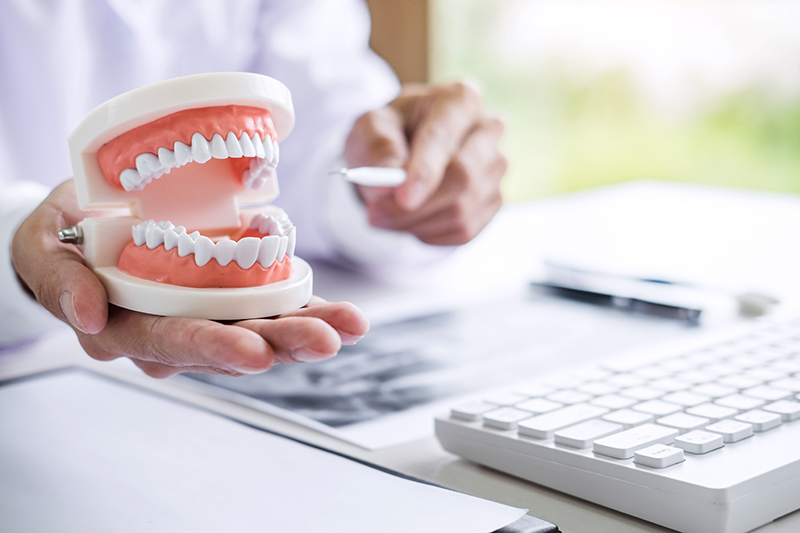

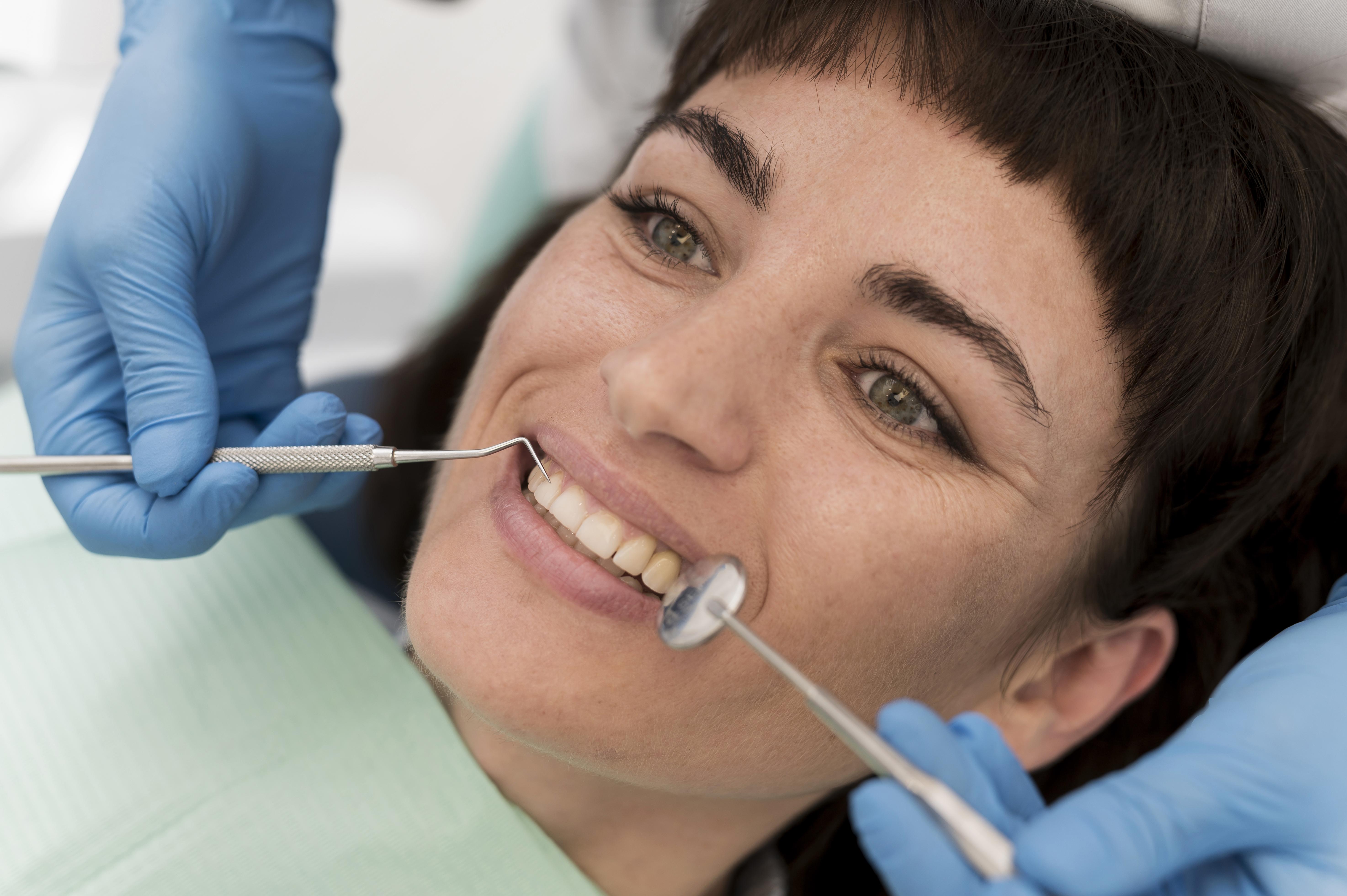
Dental implants are artificial tooth roots surgically placed in the jawbone to replace
missing teeth, serving as a strong foundation for fixed or removable replacement teeth,
like crowns, bridges, or dentures.
Here's a more detailed explanation:
What are dental implants?
• Artificial tooth roots:
Dental implants are small, typically titanium posts or screws that are surgically placed
into the jawbone to replace the root of a missing tooth.
• Foundation for replacement teeth:
Once the implant integrates with the bone (a process called osseointegration), a dentist
can attach a crown, bridge, or denture to it, providing a stable and natural-looking
replacement for the missing tooth or teeth.
• Types of implants:
• Endosteal implants: These are the most common type, placed directly
into the jawbone.
• Subperiosteal implants: These are placed on top of the jawbone, under
the gum line.
• Benefits:
• Improved chewing function: Dental implants allow you to chew and eat
comfortably, as they are fixed in place like natural teeth.
• Enhanced speech: They can improve speech by preventing dentures
from slipping.
• Improved appearance: Dental implants can restore your smile and
improve your overall appearance.
• Preservation of jawbone: They help prevent bone loss, which can occur
when teeth are missing.
• Durability: Dental implants can last for many years with proper care.
• Procedure:
• Evaluation: A dentist will assess your oral health and jawbone structure
to determine if you are a good candidate for dental implants.
• Surgical placement: The implant is surgically placed into the jawbone.
• Osseointegration: The implant fuses with the jawbone, which can take
several months.
• Abutment placement: Once the implant is integrated, an abutment (a
connector) is attached to the implant.
• Restoration: A crown, bridge, or denture is then attached to the
abutment.
A dental extraction, or "tooth extraction," is a procedure to remove a tooth from its
socket in the jawbone, often performed due to severe decay, infection, or other oral
health issues.
Here's a more detailed explanation:
Reasons for Extraction:
• Severe Tooth Decay:
When a tooth is damaged beyond repair by decay, extraction may be necessary.
• Infection:
If a tooth is severely infected, extraction might be the only way to eliminate the
infection.
• Gum Disease (Periodontal Disease):
Advanced gum disease can cause teeth to loosen and become unstable, leading to
extraction.
• Crowded Teeth:
In some cases, teeth may be removed to create space for other teeth to align
properly during orthodontic treatment.

852 Madurdaha, EKT, Kolkata 700107
Mon- Fri : 9.00 am- 12.00pm
Mon- Fri : 9.00 am- 12.00pm
Mon- Fri : 9.00 am- 12.00pm